Whether companies are making cars, semiconductor chips, smartphones, or food, having high-quality standards is essential for their business success. This is where quality control plays a major role in many industries. Ineffective quality control can lead to major operational and financial consequences, including rework, excess waste, lower output, elevated work-in-process inventory, post-sale recalls, warranty claims, and repairs.
The same applies to the manufacturing industry. By implementing effective quality control measures, manufacturers can ensure that their products are safe, reliable, and of the highest quality.
Key Aspects of Quality Control Checks Through Visual Inspection:
Visual inspection plays a key role in quality control, enabling manufacturers to ensure products meet industry standards and customer expectations. Here are the important aspects of quality control checks through visual inspection:
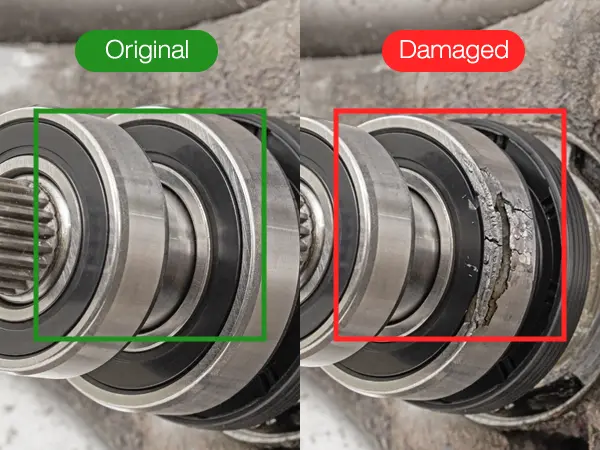
- Incoming Material Inspection: Visually inspect raw materials and components as they arrive to identify any initial defects such as discoloration, damage, or imperfections.
- In-Process Inspection: Conduct inspections during various production stages to catch defects early, such as examining alignment, surface finish, and correct part placement.
- Final Product Inspection: At the end of the production line, inspect finished products for cosmetic appearance, functional aspects, and labeling accuracy.
- Spot Checks and Sampling: Perform spot checks or sampling throughout production to monitor quality trends and address emerging issues.
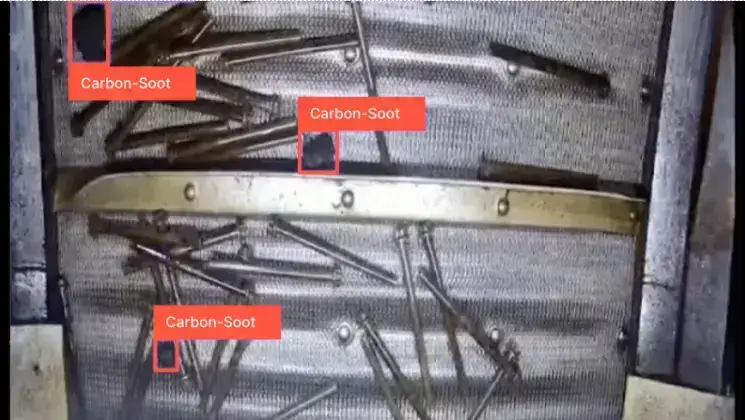
Advantages of AI Visual Inspection with a real-time example:
Visual inspection is a cornerstone of quality control in the manufacturing industry, enhancing product quality and ensuring customer satisfaction. By incorporating thorough visual inspection at every stage of production, from incoming material inspection to final product inspection, manufacturers can boost manufacturing efficiency and detect defects early. This proactive approach to quality control helps maintain high standards, protect brand reputation, and minimize costly mistakes such as product recalls and warranty claims.
Use Case: Automotive Manufacturing—Quality Control Through Visual Inspection.
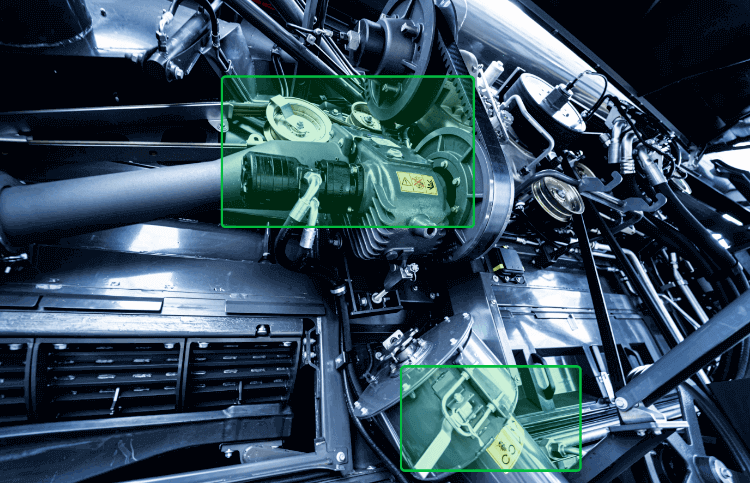
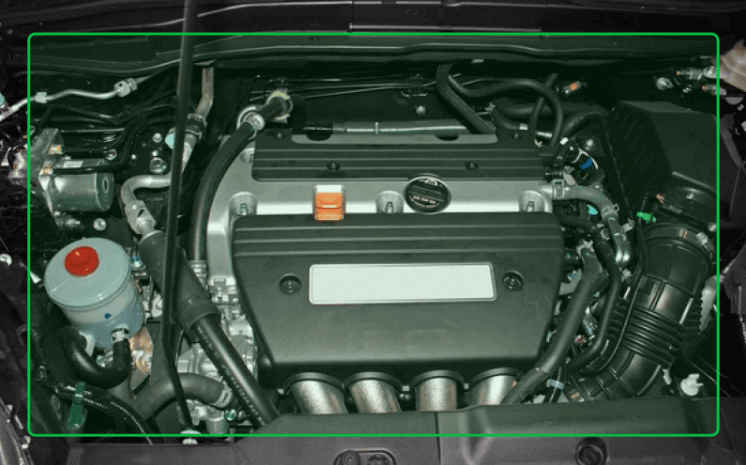
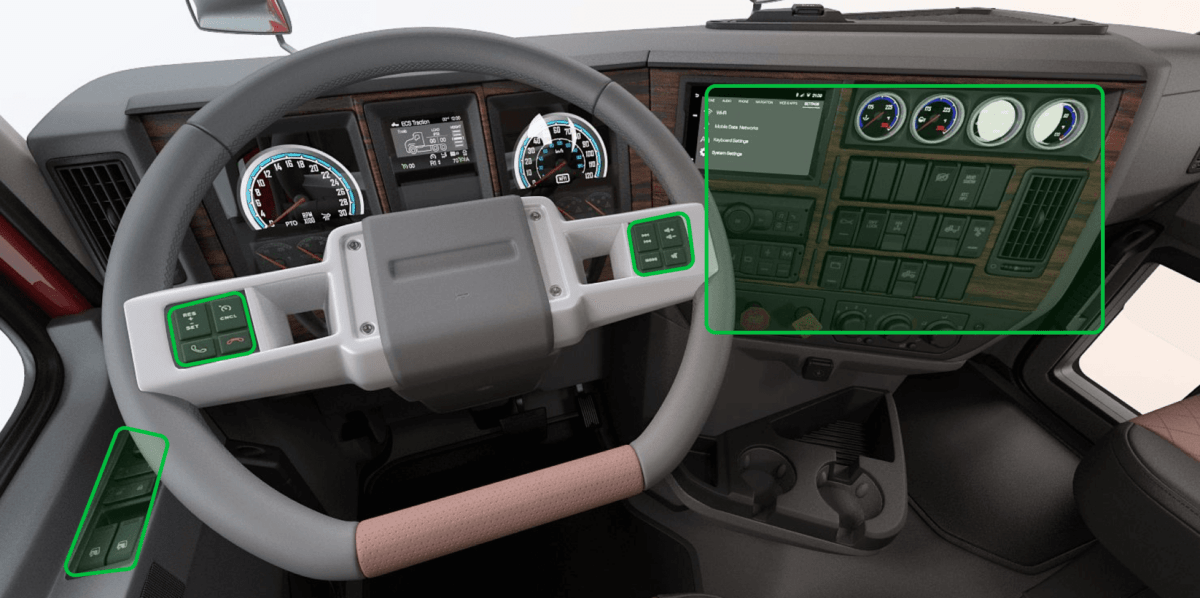
In the automotive manufacturing industry, visual inspection plays a crucial role in ensuring the quality of finished vehicles. For example, during the final assembly phase of a car, visual inspection is conducted on the vehicle’s interior and exterior. Inspectors closely examine the paint job to check for any streaks, drips, or uneven coloring. They also inspect the fit and finish of components such as doors, windows, and trims to ensure perfect alignment and smooth operation. Inside the vehicle, inspectors assess the condition of seats and upholstery for signs of damage or defects, as well as the proper installation and functionality of electronic systems like infotainment displays and controls.
This thorough visual inspection process ensures that every car leaving the assembly line meets the brand’s quality standards and customer expectations, minimizing the risk of returns or complaints. Through continuous improvement and adaptation of advanced inspection technologies, manufacturers can stay competitive and excel in their respective industries.
Futuristic Scope of Visual Inspection through AI, ML
The future of quality control in manufacturing lies in the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies into visual inspection processes. AI and ML algorithms analyze vast visual data rapidly and accurately, detecting even subtle defects missed by human inspectors. Continuously learning from new data, these systems adapt and improve over time, enhancing product quality and reducing error rates. Predictive analytics powered by AI can forecast defects before they occur, enabling proactive measures to prevent production issues. Through this synergy, manufacturers can achieve greater precision, efficiency, and customer satisfaction.